

Remember, if any one of these seven are not proven beyond a reasonable doubt, the case cannot continue.ġ. Below are the seven issues of jurisdiction in any and every court case.
JURISDICTION AS ELEMENT OF CRIME TRIAL
To allow the trial to continue at all is to admit to jurisdiction. If jurisdiction is to be successfully challenged, it must be at the commencement of proceedings, but it can be challenged at any time. If any element of the seven is not proven on the record, the case must be dismissed. If not challenged, it will ALWAYS be assumed by the court that competent jurisdiction is proved and accepted by all parties.
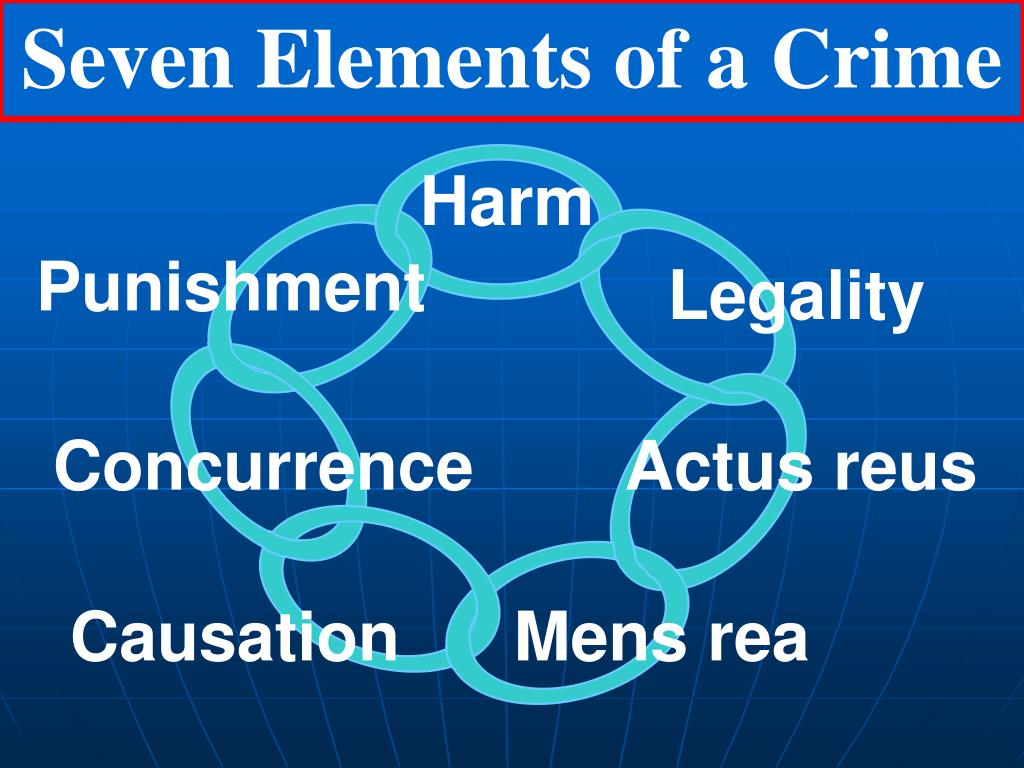
There are seven elements of jurisdiction, all of which must be proved by the prosecution if challenged. But to win, jurisdiction MUST be challenged by the individual, and if challenged successfully, the case is dismissed. In fact, jurisdiction is almost never even addressed. Specifically, before an individual can be charged and convicted with a crime, the government official or agency must prove jurisdiction. Same Script,Tactics, & Players - 10 years Prior -Video.Martial Law Under the General Orders No.Admiralty Law- History of the Law of the Sea, Guilty until Proven Innocence.For a state court to hear this case, that court will typically need to satisfy the constitutional due process requirement for territorial jurisdiction (see above) as well as the state statutory requirement, which is typically known as a state's long-arm statute. Parties will often sue a defendant who is a resident of a different state. An example showing the interplay of diversity jurisdiction with subject-matter jurisdiction is Grupo Dataflux v. Other forms of jurisdiction include appellate jurisdiction (the power of one court to correct the errors of another, lower court), concurrent jurisdiction (the notion that two courts might share the power to hear cases of the same type, arising in the same place), and diversity jurisdiction (the power of Federal courts to hear cases in which the parties are from different states). State court territorial jurisdiction is determined by the Due Process Clause of the Constitution's Fourteenth Amendment and the federal court territorial jurisdiction is determined by the Due Process Clause of the Constitution's Fifth Amendment. This law determines the scope of federal and state court power. Territorial jurisdiction is the court's power to bind the parties to the action. Federal courts have limited jurisdiction in that they can only hear cases that fall both within the scope defined by the Constitution in Article III Section 2 and Congressional statutes (See 28 U.S.C. State courts have general jurisdiction, meaning that they can hear any controversy except those prohibited by state law (some states, for example, deny subject matter jurisdiction for a case that does not involve state citizens and did not take place in the state) and those allocated to federal courts of exclusive jurisdiction such as bankruptcy issues (see 28 U.S.C. Subject matter jurisdiction is the court's authority to decide the issue in controversy such as a contracts issue, or a civil rights issue. Such a legal question is referred to as "jurisdiction to determine jurisdiction." The question of whether a given court has the power to determine a jurisdictional question is itself a jurisdictional question. The term jurisdiction can be best understood by being compared to "power." Any court possesses jurisdiction over matters only to the extent granted to it by the Constitution, and/or legislation of the sovereignty on behalf of which it functions (ex: a state court in Mississippi may need statutory permission by the Mississippi legislature to hear certain types of cases). whether there is jurisdiction to render the particular judgment sought.whether there is jurisdiction over the subject matter.This is further broken down into 3 categories (See Pennoyer v. whether there is personal jurisdiction.A jurisdictional question may be broken down into three components: One of the most fundamental questions of law is whether a given court has jurisdiction to preside over a given case. Territory within which a court or government agency may properly exercise its power.Power of a court to adjudicate cases and issue orders.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
